Gum Disease Symptoms You Should Never Ignore

Gum Disease Symptoms You Should Never Ignore - Enzim Singapore
Introduction: Why Symptoms Matter
Gum disease, a prevalent oral health condition worldwide, often goes undetected until it reaches advanced stages. Often referred to as a "silent disease," its early warning signs can be subtle. Many individuals dismiss mild bleeding or redness, only to discover years later that the condition has progressed into advanced periodontal disease.
Globally, millions live with untreated gum problems. In fact, gum disease is caused by harmful oral bacteria that thrive in dental plaque and calculus (also known as tartar). Left unchecked, the infection spreads beneath the gums, leading to gum recession, bone loss, and eventually tooth loss.
So, what does gum disease look like in its early and advanced stages? Let's explore the symptoms you should never ignore, and why recognizing them could save both your smile and your overall oral health.
1. Bleeding Gums: The First Warning Sign
The earliest symptom of gum disease is often bleeding gums. Healthy gums should not bleed during routine oral hygiene practices. If they do, it means your gum tissue is inflamed and vulnerable.
Bleeding Gums When Brushing
If you experience bleeding while brushing, it is a clear indicator that bacteria are irritating your gumline. While some believe this is normal, it should always be taken seriously as a sign of potential gum disease.
Gums Bleeding and Gingival Bleeding
Dentists refer to this condition as gums bleeding or gingival bleeding. It happens because plaque and calculus build up where your toothbrush, interdental brushes, or floss cannot reach, irritating tissues. If ignored, these symptoms can evolve into deeper gum infections that require professional intervention.
2. Swollen and Inflamed Gums
Another early red flag of gum disease is swelling or puffiness of the gums.Swollen gums often look red and feel tender to the touch. They may also bleed during meals or brushing, indicating the early stages of gum disease.Persistent gum swelling is caused by plaque and tartar toxins. This swelling makes it easier for bacteria to penetrate deeper into gum tissue, potentially leading to more severe forms of gum disease. When redness and puffiness persist, you're dealing with inflamed gums. Dentists call this gingival inflammation, and it's one of the first signs of gingivitis. Without proper oral hygiene and care, it may advance to periodontitis and periodontal inflammation, more serious stages of gum disease.
Sometimes people mistake swollen gum tissue for irritation from food, orthodontic appliances, or even aggressive brushing. While those can cause temporary puffiness, true gum swelling linked to gum disease is persistent. If the tissue stays enlarged, red, and tender for more than a few days—even after adjusting your hygiene—it is a sign of deeper infection. Visiting a dentist appointment at this stage can prevent progression to periodontitis.
3. Gingivitis Symptoms
Gingivitis is the earliest and mildest form of gum disease. It is completely reversible if treated early with good oral hygiene practices.
Gingivitis
Typical symptoms of gingivitis include redness, gum tenderness, bleeding, and sometimes bad breath. These signs may be minor but should never be ignored as they can progress to more severe forms of gum disease.
Gingival Pocket Formation
If gingivitis worsens, you may develop gingival pockets—small separations where gums start pulling away from teeth. These pockets are breeding grounds for bacteria and can progress to periodontal pockets, a more serious sign of advancing gum disease.
Prevent Gingivitis
With good oral hygiene and professional care, you can prevent advancing to more severe forms of gum disease. This includes daily flossing, using interdental brushes, brushing teeth twice daily with fluoride toothpaste, using an antimicrobial mouthwash, and attending regular dental cleaning appointments.
4. Gum Recession and Gingival Recession
As gum disease progresses, gum tissue begins to pull back, exposing sensitive tooth rootsGum recession makes teeth appear longer and increases sensitivity to temperature and sweetness. This is a clear sign of advancing gum disease that requires attention. Unlike gingivitis, gingival recession cannot repair itself naturally. Early gum treatment is vital to prevent further tissue loss and halt the progression of gum disease.
5. Periodontal Symptoms
When gum disease enters the periodontitis stage, it begins affecting the supporting structures of teeth, leading to periodontal inflammation.
Periodontal Pocket
A deepened space between teeth and gums, usually greater than 4mm, is called a periodontal pocket. Dentists measure this using a periodontal probe during a dentist appointment or dental cleaning to assess the severity of gum disease.
Gum Pockets
Gum pockets trap food and bacteria, making it nearly impossible to clean at home. Over time, these deepen, causing attachment loss and eventually loose teeth, signifying advanced gum disease.
Perio and Periodontal Disease
Dentists often use the term perio to describe periodontal treatment. Symptoms at this stage of gum disease include persistent bleeding, bad breath, and even pus near the gumline.
6. Advanced Gum Disease
When symptoms are ignored, gum disease progresses to its most destructive stages.
Pyorrhea
Pyorrhea involves significant bone loss and tooth instability. Teeth may feel loose or shift in position, indicating severe gum disease.
Necrotizing Gingivitis
A rare but severe symptom of advanced gum disease, where gum tissue begins to die. This condition causes extreme pain, foul odor, and ulcers. It often occurs in patients with compromised immunity, poor nutrition, or extreme stress.
Dental Disease Complications
At this stage, gum problems merge with other dental diseases, increasing risks of abscesses, tooth loss, and systemic complications related to severe gum disease.
Beyond tooth loss, advanced gum disease can affect daily life significantly. Chewing becomes difficult, which may lead to poor nutrition. Some patients report constant discomfort, oral pain, or embarrassment due to shifting teeth and visible gum changes. Others struggle with chronic halitosis that affects social interactions. These lifestyle consequences show why ignoring gum disease symptoms is never an option.
7. Systemic and Whole-Body Symptoms
Gum disease doesn't just affect your mouth—it can impact your entire body and overall oral health.
Bad Breath and Metallic Taste
Persistent halitosis (bad breath) and an unpleasant metallic taste are common systemic symptoms linked to gum infections and advanced gum disease.
Oral Bacteria and Systemic Inflammation
Harmful oral bacteria can travel into the bloodstream, fueling systemic inflammation. This connection between gum disease and overall health has been linked to cardiovascular disease, heart disease, diabetes, and even respiratory infections.
Inflammatory Disease Link
Chronic gum disease also contributes to wider inflammatory disease, potentially worsening conditions like arthritis or autoimmune disorders.
8. Professional Diagnosis
Recognizing symptoms is important, but professional diagnosis ensures accurate treatment of gum disease.
Dental Plaque Detection
Dentists first check for visible dental plaque or plaque buildup at the gumline. They may also look for calculus or tartar formation, which are key contributors to gum disease.
Periodontal Probe and Dental X-Rays
Using a periodontal probe, dentists measure pocket depth to assess gum disease severity. Dental x-rays reveal hidden bone loss and the extent of gum disease infection.
Gum Specialist Consultation
If symptoms are advanced, you may be referred to a gum specialist (periodontist) or dental hygienist. They offer advanced solutions for severe gum disease such as LANAP or guided tissue regeneration.
9. Treatment Indicators
Certain symptoms signal the need for immediate gum disease treatment.
Gum Treatment Options
Mild gum disease may be reversed with gum treatment like scaling, deep cleaning, and professional cleaning by a dental hygienist.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Moderate gum disease symptoms are often managed with non-surgical treatment such as root planing, antibiotics, or medicated mouth wash.
Advanced Options
In cases of attachment loss or bone loss due to severe gum disease, advanced procedures such as LANAP, grafting, or surgery are required.
Gum disease treatment doesn’t end after one session of cleaning or therapy. Regular follow-ups with your dentist or periodontist are crucial. These visits allow professionals to measure pocket depth again with a periodontal probe, monitor for calculus buildup, and adjust treatment plans. Patients who attend follow-up care maintain healthier gum tissue and are less likely to relapse into severe gum disease.
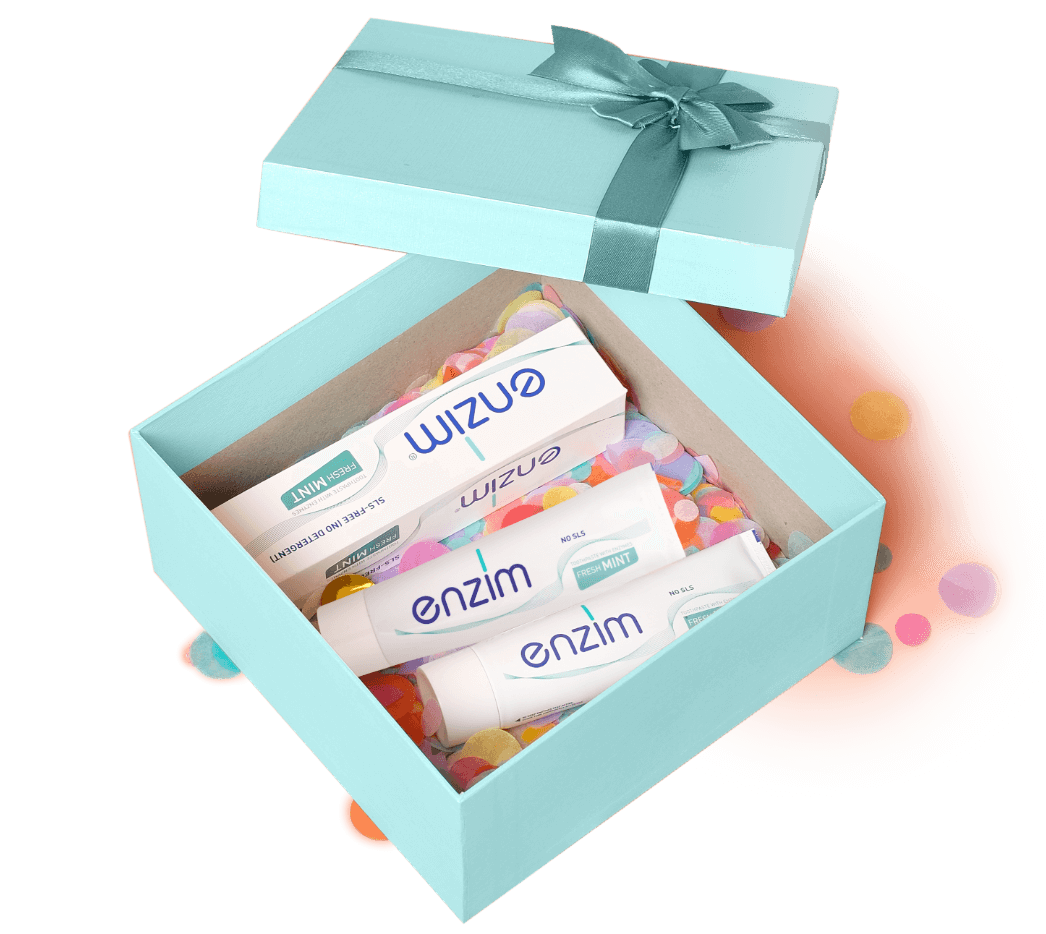
10. Enzim Toothpaste: Daily Prevention of Symptoms
The best way to manage gum disease is prevention—and that starts with the right oral hygiene routine and toothpaste.
Enzim enzyme-based toothpaste is SLS-free and enriched with active enzymes like lysozyme and lactoferrin, which strengthen saliva's natural antibacterial system. While it's not a fluoride toothpaste, it offers unique benefits for gum health and gum disease prevention.
It helps by:
-
Preventing gingival bleeding and irritation
-
Reducing dental plaque buildup and tartar formation
-
Protecting against gum swelling and gingival recession
-
Helping maintain healthy gums
-
Supporting patients with food-grade, halal-certified safety
Daily use of Enzim, along with proper brushing, flossing, and use of interdental brushes, reduces the risk of gum disease progressing from mild to severe.
Final Thoughts
Bacteria cause gum disease, but the symptoms appear long before teeth become loose or fall out. From bleeding gums and inflamed gums to gum pockets and necrotizing gingivitis, each sign is a reminder to take action against gum disease.
Recognizing these symptoms and acting early is the key to protecting both your smile and your overall health. With regular dental visits, professional care from a dental hygienist, and a comprehensive oral hygiene routine including Enzim enzyme-based toothpaste, you can prevent gum disease from taking hold and maintain excellent oral health. Understanding what causes gum disease and how to prevent it is crucial for long-term oral health maintenance.